你也需要一个Agent
基于LangChain打造一个K8s魔法师
在大模型时代,借助大模型的能力我们可以实现更加智能的应用,本文介绍基于LangChain框架如何构建一个Kubernetes的AI Agent。更多关于大模型的应用开发,可以参考大模型时代。
KubeWizard是一个基于大模型(LLM)的K8s自动运维工具,可以自动诊断问题、管理资源,效果如下:
Agent是什么
Agent本意是代理人,比如房屋中介,能代替人做部分事情。具体到LLM Agent目前没有一个统一的定义,常翻译为智能体,通常指能够感知环境、自动决策并执行动作的智能实体。
下图是一个LLM Agent认可较广的架构: 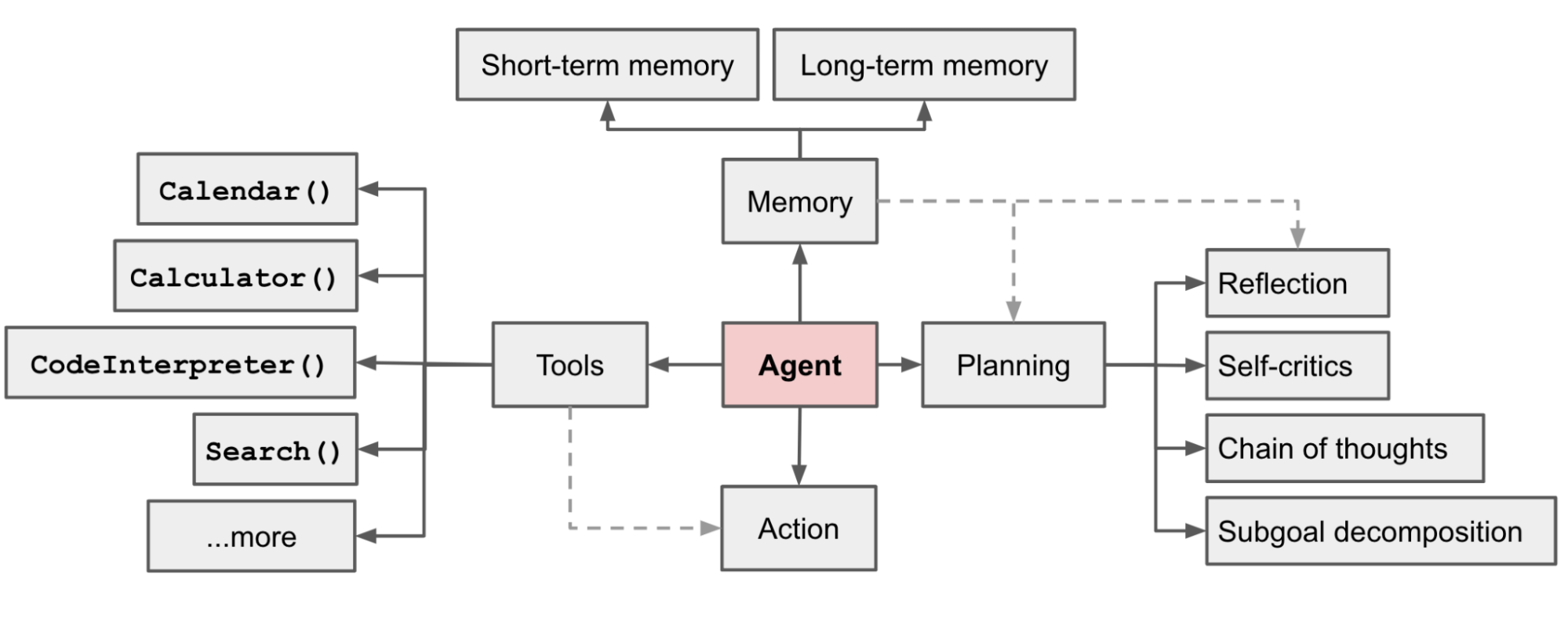
LLM Agent可以用公式定义为:
Agent = LLM + Planning + Action + Tools + Memory
智能体能够实现复杂任务的规划,可以借助外部工具执行每一个步骤,根据执行结果不断调整,并将结果记录存储起来,最终完成任务。拆开来看:
- LLM:LLM作为智能体的大脑,可以实现任务的规划、根据执行结果进行反思。
- Tools: 由于LLM本身的局限,借助外部工具赋予智能体双手,可以根据任务步骤做出行动,如查询天气、执行代码、搜索内容。
- Memory: 智能体可以记忆过去的经验,这对学习至关重要,可以根据这些先前的经验调整未来的行动。
借助智能体我们可以实现更加智能化、多步骤的任务,控制流是由LLM制定的,并不是人类经验的硬编码。使用Agent可以实现数据分析、智能个人助手、自动运维工具等。
如何实现Agent
ReAct
Agent的核心是使用LLM的规划、反思能力,开发Agent最常用的设计模式是ReAct(Reasoning + Acting),LLM生成推理轨迹、执行特定动作,然后根据执行结果不断调整计划,最终实现任务。
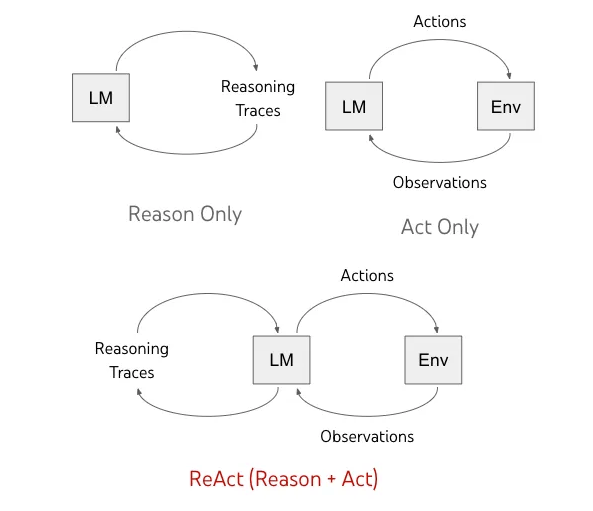
ReAct很像人类解决问题的过程,首先我们会做一个大体的规划,然后开始实施,根据结果不断调整,从而最终达到目的。
- Reason Only:典型地如
COT(Chain of Thought),无法感知环境,只能解决有限的问题(数学题,简单的逻辑推理)。 - Act Only:如果只根据规划做出动作,前面步骤的失败会造成整体任务失败。
ReAct结合推理与行动,使得LLM能够根据当前的观察和过去的经历,形成一套行动计划,并在执行过程中不断调整和优化这一计划。通过将决策制定过程分解为一系列可解释的步骤,ReAct增强了系统的透明度和可理解性。
除了ReAct模式外,还有其他诸如Plan & Execute、Multi-Agents等。
Function Calling
Agent的另一个重点是能够借助工具感知环境,比如借助搜索引擎获取最新数据、通过API来查询所需数据,甚至执行具体命令,借助工具Agent的边界会大大拓宽。
Function Calling是LLM提供一项扩展能力,是指模型在响应用户请求时,可以返回合适的预定义的函数及其参数,目前大部分模型已经支持。
比如可以预定义一个天气函数
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
},
}
]
如果询问大模型北京的天气怎么样,会返回如下结果:
ChatCompletionMessage(content=None, role='assistant', function_call=FunctionCall(arguments='{\n "location": "北京"\n}', name='get_current_weather'), tool_calls=None)
有了Function Calling的能力,可以无限扩展LLM。除此之外,我们也可以通过设计Prompt来让大模型返回所需要调用的工具和参数。
LangChain是什么
LangChain是一个开源的大模型应用开发框架,可以帮助开发者快速构建LLM应用。
为什么需要LangChain
有了诸如GPT4这么强大的LLM和Function Calling,为什么我们还需要大模型框架呢?想象以下问题:
- 我要对接多个大模型怎么办,每个API都不同?
- 怎么对接各种工具和向量数据库?
- 输入输出怎么样结构化?
- 如何组织复杂的LLM调用链?
这便是LangChain存在的价值,通过对接多种LLM、工具,可以方便的开发RAG、Agents等大模型应用。
LangChain的缺点
LangChain为了适配各种情景,做了高度抽象,无法满足灵活的定制,而且调试和测试比较困难。对于简单的应用,复杂度较高,对于复杂的应用又缺少生产环境的验证。
构建Agent应用
接下来就是如何构建Agent,主要考虑ReAct的实现、工具,剩下的就交给LangChain了。
我们的目标是实现一个K8s智能运维工具,社区中已经有一些k8s-gpt、kubectl-ai等K8s生态的AI助手,但都太初级了,需要大量编码或者只能解决非常有限的场景。
Prompt
ReAct是Agent的灵魂,可以使用Prompt来实现:
prompt = """
You are a Kubernetes expert. A user has asked you a question about a Kubernetes issue they are facing. You need to diagnose the problem and provide a solution.
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
{tools}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}].
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
When you have a response to say to the Human, or if you do not need to use a tool, you MUST use the format:
---
Thought: Do I need to use a tool? No
Final Answer: [your response here]
---
Begin!
Previous conversation history:
{chat_history}
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}
"""
- 首先,是一段系统指令,告诉LLM应该扮演一个K8s专家的角色;
- 其次,说明可以使用的工具集,包含相关参数;
- 接着,使用
ReAct的思想进行思考,通过多次执行Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation; - 最后,设置中止条件,如果不需要执行工具就结束。
Tools
KubeWizard首先需要执行kubectl命令,定义一个LangChain的Tool,设置工具的名字、描述、参数等,核心是在_run中调用ShellTool来执行命令,具体定义如下:
class KubeInput(BaseModel):
"""Args for the k8s tool."""
commands: str = Field(
...,
example="kubectl get pods",
description="The kubectl/helm related command to run.",
)
""" Kubectl commands to run."""
class KubeTool(ShellTool):
name = "KubeTool"
"""Name of tool."""
description = "Tool to run k8s related commands(kubectl, helm) on the Kubernetes cluster. The input is the string command to run."
"""Description of tool."""
args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = KubeInput
def _run(
self,
commands: str,
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForToolRun] = None,
) -> str:
"""Run commands and return final output."""
commands = self._parse_commands(commands)
return super()._run(commands)
def _parse_commands(self, commands: str) -> str:
"""Parse commands."""
return commands.strip().strip('"`')
另外需要获取K8s的最新信息,比如版本、API是否废弃等,就需要有搜索、阅读网页的能力,这里实现了搜索工具与请求工具。
搜索基于DuckDuckGo,API是免费但效果要比Google、Bing差一些,LangChain已经封装好了,可以直接使用
def create_search_tool():
return DuckDuckGoSearchResults(
description="""
Search the web for information on a topic, there are some useful websites for k8s info:
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/: Official Kubernetes documentation
- https://kuberentes.io: Kubernetes community site
- https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes: Kubernetes GitHub repository
""",
api_wrapper=DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper(
max_results=10,
time="y",
backend="api",
source="text"
)
)
请求使用了BeautifulSoup、html2text来处理网页,如下:
class RequestsGet(RequestsGetTool):
name = "RequestsGet"
description = """A portal to the internet. Use this when you need to get specific
content from a website. Input should be a url (i.e. https://www.kubernetes.io/releases).
The output will be the text response of the GET request.
"""
requests_wrapper = TextRequestsWrapper()
allow_dangerous_requests = True
parser = HTML2Text()
parser.ignore_links = True
parser.ignore_images = True
parser.ignore_emphasis = True
parser.ignore_mailto_links = True
def _run(self, url: str, **kwargs: Any) -> str:
response = super()._run(url, **kwargs)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response, 'html.parser')
for tag in soup(['header', 'footer', 'script', 'styple']):
tag.decompose()
data = self.parser.handle(soup.prettify())
return data
此外,还将Human做为一个特殊工具,如果需要额外信息可以由人工提供,执行危险操作时,需要人类确认。
Agent
LangChain提供了多种Agent类型,如OpenAI Tools、JSON Chat、Tool Calling等,这里使用ReAct类型。创建过程如下:
# 定义工具
tools = [KubeTool(), KubeToolWithApprove(), human_console_input(), create_search_tool(), RequestsGet(allow_dangerous_requests=True)]
# 设置Prompt
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(REACT_PROMPT, tools=tools)
# 默认模型使用的gpt-4o-mini
def __init__(self, llm: BaseChatModel= ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0.7), debug_level: Optional[int] = None):
# 内存来记录会话
self.memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history")
# 创建agent
agent = create_react_agent(llm, self.tools, self.prompt)
verbose = False
return_intermediate_steps = False
# 创建执行器,最终来调用agent
self.agent = AgentExecutor(
name=self.name,
agent=agent,
memory=self.memory,
tools=self.tools,
return_intermediate_steps=return_intermediate_steps,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
verbose=verbose,
)
使用时,只需要通过invoke函数来传递输入:
def invoke(self, input: str):
return self.agent.invoke({
"input": input,
"chat_history": self.get_chat_messages(),
})
然后使用rich库构建了一个交互式终端,可以与KubeWizard交互。
效果
在文章开头提供了例子里面,通过创建了一个selector有问题的Service,KubeWizard通过多次调用KubeTool获取了Service、Pod、Pod/Log信息,最终排查到是selector有问题。并提供了修复方法,由于修复需要修改资源,所以调用KubeToolWithApprove工具请求批准,最终解决了问题,这个过程完整自动化,和我们自己排查轨迹基本一致。非常的Amazing,在之前我们比如把这些思路硬编码才能实现类似的功能。
再来看一个例子,询问当前集群可升级到的最新patch版本,别看这个问题简单,如果是你需要几步才能完成这个操作。
kubewizard>: 当前集群可升级到的最新patch版本
> Entering new KubeAgent chain...
To determine the latest patch version that the current Kubernetes cluster can be upgraded to, I can check the current version of the cluster and then look for available updates.
Action: KubeTool
Action Input: kubectl version --short
Executing command:
kubectl version --short
error: unknown flag: --short
See 'kubectl version --help' for usage.
I made an error in using the `--short` flag, which is not a valid option for the `kubectl version` command. Instead, I will run it without the flag to get the current version of the Kubernetes cluster.
Action: KubeTool
Action Input: kubectl version
Executing command:
kubectl version
Client Version: v1.30.2
Kustomize Version: v5.0.4-0.20230601165947-6ce0bf390ce3
Server Version: v1.28.3
WARNING: version difference between client (1.30) and server (1.28) exceeds the supported minor version skew of +/-1
To find the latest patch version that the current Kubernetes cluster (version 1.28.3) can be upgraded to, I will check the available patch versions for Kubernetes 1.28.
Action: RequestsGet
Action Input: https://kubernetes.io/releases
The Kubernetes project maintains release branches for the most recent three
...
### 1.28
Latest Release: 1.28.12 (released: 2024-07-16 )
End of Life: 2024-10-28
Patch Releases: 1.28.0 , 1.28.1 , 1.28.2 , 1.28.3 , 1.28.4 , 1.28.5
, 1.28.6 , 1.28.7 , 1.28.8 , 1.28.9 , 1.28.10 , 1.28.11 , 1.28.12
...
---
Thought: Do I need to use a tool? No
Final Answer: The latest patch version that your current Kubernetes cluster (version 1.28.3) can be upgraded to is 1.28.12.
---
> Finished chain.
例子中,第一步获取版本信息失败,但第二步经过反思后就获取到版本,再通过RequestTool获取最新的版本信息,从而得到最新的patch版本是1.28.12。为什么这里不用使用搜索就知道需要访问的页面,如果在RequestTool的描述里取代K8s相关页面,就会先调用SearchTool再调用RequestTool。
所有源码见https://github.com/qingwave/kubewizard。
总结
本文介绍了Agent的概念、原理,以及如何通过LangChain来打造一个K8s魔法师自动运维工具KubeWizard。
曾几何时,我们也幻想过AI能否替代人类做一部分工作,大模型时代,好像未来并不遥远。展望一下未来,具有意识和情感的智能体有没有可能在不远的将来出现呢。
Explore more in https://qingwave.github.io